Additionally, variable costs influence calculations of gross margin, profit margin, and net income, making them fundamental to profit assessments. By tracking variable expenses like raw materials and direct labor, businesses can adjust operations to control costs, optimize profitability, and improve overall financial decision-making. In business, the term “variable variable cost costs” refers to those expenses that change concerning the amount of goods or services produced. Variable costs increase or decrease as production increases or decreases. Common examples of variable costs include raw materials, commissions, and direct labor. The total variable cost is the sum of all these individual variable expenses.
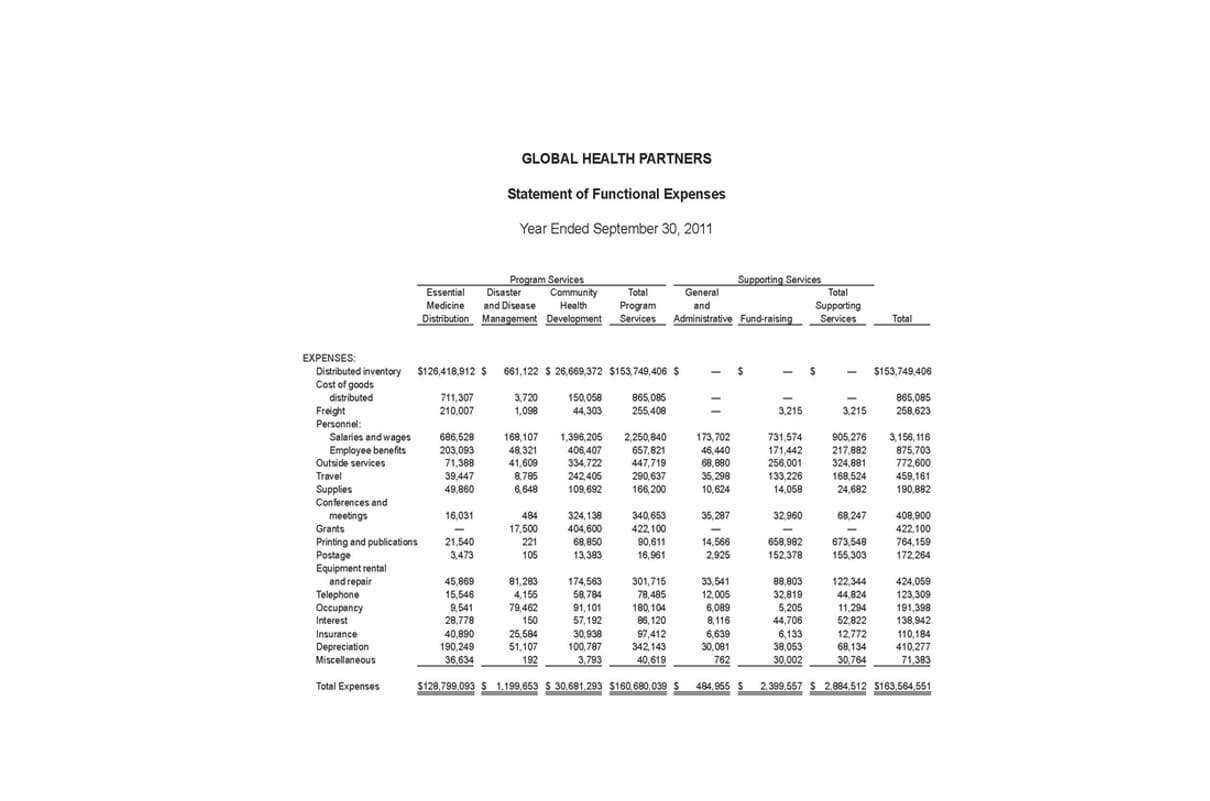
Calculating Net Operating Income with Variable Costing
By now, it’s evident that variable costs aren’t just mere numbers on a balance sheet; they play a dynamic role in shaping the direction and success of a business. It’s important to remember that your normal balance costs and selling prices will change over time. For this reason, it’s a good idea to calculate your breakeven point regularly to adjust your sales goals accordingly.
How To Calculate Variable Expenses (With Examples)

Fixed costs are those expenses that remain constant regardless of how much or how little you produce. In other words, they’re not directly affected by changes in production volume. Fixed costs include rent/mortgage, insurance, property taxes, interest on loans, depreciation, legal fees, and accounting fees.
Does variable cost include overhead expenses?
Marginal cost represents the overall change in the total cost of production when a company increases its production by one unit. Unlike variable costs, marginal costs account for both fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs stay the same regardless of production, and you can generally count on them staying that way. Understanding the total variable costs and the fixed costs of your business is important for a variety of different reasons.
- Reducing variable costs involves a combination of strategic sourcing, process optimization, and other such strategies.
- Variable expense, on the other hand, depends on production levels.
- Variable costing is a concept used in managerial and cost accounting in which the fixed manufacturing overhead is excluded from the product-cost of production.
- This example shows how variable costs change with production levels, providing businesses with insights into how scaling up or down will impact costs.
- Learn essential tips, tricks, and strategies to ace every calculation and impress in your consulting interviews.
- This method is useful for management decision-making, as it provides a clearer picture of the impact of changes in production levels on costs and profitability.
If you’re looking for support with tracking all the costs that go into making your business possible, FreshBooks accounting software can help. With in-depth expense tracking, powerful reporting features, and around-the-clock support, we can support your business as it scales up and reaches new heights. For SaaS companies, understanding AVC allows them to align their pricing with financial goals. This makes sure that metrics like Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) remain healthy. Variable costing can provide useful insights for internal decision-making, but businesses must balance it carefully with external reporting needs and understand cost behaviors. For example, Suzi is quite worried about her cafe since the sales revenue is less than the overall cost of operating the cafe.

Variable costs: A comprehensive guide + variable cost formula

The break-even point is the level of production at which the company’s total revenue equals its total costs. One useful tool for analyzing profit margins is contribution margin analysis. This analysis calculates the contribution margin, which is the amount of revenue that is left over after deducting variable costs. Remote Bookkeeping By analyzing the contribution margin, businesses can identify which products or services are most profitable and make informed decisions about their product mix.
- Next, add the values for the number of units made during the chosen week.
- Keep an ear to the ground for market trends and be ready to pivot.
- This supports data-driven planning and decision making leveraging variable costing insights.
- Variable expenses do not remain consistent if the output product changes.
- You’ll need variable cost data to make the right decision in this scenario, which will greatly impact profitability and leverage.
- To calculate the variable cost of each item you sell, add up every expense directly related to creating it—the variable cost per unit.
For example, in electronic gadget manufacturing, components like microchips and batteries represent variable costs. These costs can shift based on market conditions, supplier pricing, and production efficiency. Understanding these factors is essential for accurately calculating both variable cost per unit and total variable costs. Variable costs fluctuate as output levels change, as was previously noted. Contrarily, fixed costs are expenses that are consistent independent of the amount of production (like office rent).
What Is the Difference Between a Variable Cost and a Fixed Cost?
The business should ensure that the average cost is always lower than the prices so that the revenue earned is able to cover the cost or production, leading to profits. In the long run, however, the business tries to achieve the revenue level, which covers both average variable cost and fixed cost. The contribution margin is your product’s selling price minus its variable cost per unit. This measurement is the money your company brings in after using sales to cover variable costs. If your product has a proportionately lower variable cost than its selling price, then it has a high contribution margin.