
From the perspective of regulatory bodies, there is a push towards greater transparency and consistency. This means that the criteria for income realization may become more stringent, requiring more verifiable evidence that services have been rendered or goods delivered. From an accountant’s perspective, the realization principle prevents the premature recognition of income, which could otherwise inflate earnings and mislead stakeholders. For auditors, it serves as a guideline for verifying the timing and amount of revenue reported. Investors and analysts rely on this principle to assess the true economic performance of a company, free from the distortions of cash timing discrepancies.
Matching Principle & Concept
- SaaS companies also use a modified version of the installment method when recognizing revenue over the course of a subscription period.
- Under this method, all revenue and expenses are recorded only upon completion of the contract.
- This approach contrasts with cash-basis accounting, where revenue is recorded only when cash is received, and expenses are recorded when cash is paid.
- Both principles have their merits and limitations, and the decision of which to apply often depends on the specific circumstances and financial policies of a business.
In practice, this means that revenue is recorded https://www.bookstime.com/articles/single-step-vs-multi-step-income-statement when the underlying service or sale is complete, signifying a critical point where the risks and rewards of ownership have been transferred to the buyer. In the realm of accounting, the Realization Principle and Recognition Principle are cornerstones for understanding when and how income should be recorded. These principles guide accountants in determining the appropriate timing for acknowledging revenue, ensuring that financial statements provide a true and fair view of a company’s financial performance.
Improving business decision-making 🔗

It provides a more consistent and comparable view of financial health over time, as it smooths out the timing differences between earning revenue and receiving cash. According to the Realization Principle, the publisher cannot recognize the entire subscription fee as revenue upon receipt. Instead, the revenue is recognized monthly as each magazine issue is delivered, aligning the revenue with the period in which it is earned. So, the revenue needs to be recorded on 20th March because risk and rewards have been transferred on this date. While the Realization Principle concerns when revenue should be recognized in the income statement, cash flow refers to the net amount of cash and cash equivalents being transferred into and out of a business.
Practical Applications in Business Accounting
This is particularly true in industries where income is earned over time or where the delivery of goods and services is not concurrent with payment. The timing of income recognition can significantly impact reported earnings, influencing investor perceptions and business decisions. The concept of realization is interpreted and applied differently across various accounting frameworks, reflecting the diverse regulatory environments and economic contexts in which businesses operate. In the United States, the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) emphasize the realization principle as a cornerstone of revenue recognition.
- This means that a company might recognize revenue from a sale even if the payment is expected in the future.
- Regulators know how tempting it is for companies to push the limits on what qualifies as revenue, especially when not all revenue is collected when the work is complete.
- The Realization Principle is a cornerstone of accrual accounting, which is widely adopted in international accounting practices.
- A business might have recognized revenue when it delivered the goods or provided the service, but the actual payment might not come until later, such as when the customer pays the bill or settles an invoice.
- In today’s competitive and dynamic market, understanding the needs and preferences of customers is…
- Uncle Joe thinks your idea is so cool and places an order for 10 cups of lemonade even before you open shop.
Revenue Realization

Under GAAP, revenue is realized when it is earned and realization principle accounting there is reasonable assurance of collectability. For example, a software company may recognize revenue when it sells a software license to a customer. However, revenue realization may occur over a period of months or years as the customer uses the software and pays for ongoing support and maintenance.
Realization vs. cash receipt: What’s the difference? 🔗
The realization principle states that when a business sells goods, the revenue will be recognized at the time the seller transfers the risk and rewards of owning the goods to the buyer. The revenue realization rate is the percentage of expected or forecasted revenue that is actually realized by a business. Under this method, all revenue and expenses are recorded only upon completion of the contract. This method is a lot more straightforward but can lead to large fluctuations in financial results since revenue is recognized only at the end of the project.
Accrual Concept
- The timing difference between realization and recognition can have significant implications for financial reporting.
- From the perspective of a business owner, the Realization Principle helps in forecasting and managing cash flow by aligning revenue with the actual delivery of goods or services.
- In either case, only the percentage of services that have been completely delivered is realized as revenue every month or year.
- Timing is a critical factor in revenue recognition, as it can significantly impact a company’s financial statements and overall financial health.
Providing training and education to employees on revenue recognition policies and procedures to ensure consistency and accuracy. Typically, this will happen when the business has rendered the services or transferred the goods to the customer. Revenue recognition is the identifying of revenue to be admitted to a given year’s income statement. Most often, revenue realisation and recognition occur contemporaneously and are recorded concurrently, i.e., in the same entry. Realisation, however, cannot take place by the holding of assets or as a result of the production process alone.
Realization Principle: Realization Principle: The Prudent Recognition of Income
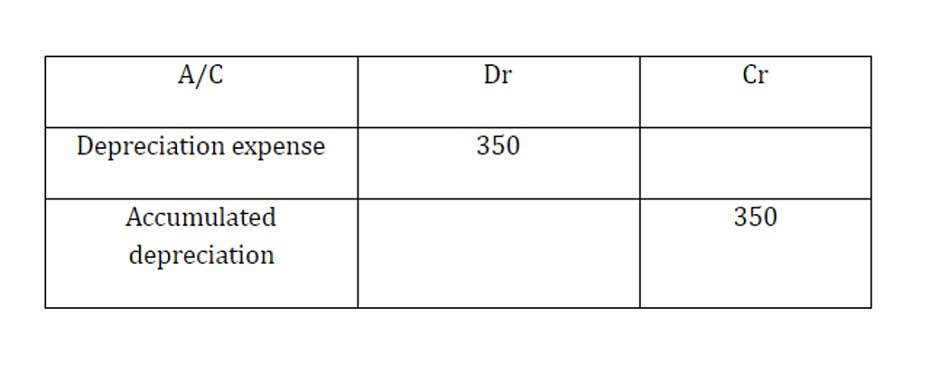
The realization principle’s applications in business accounting are diverse and play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting. It allows for income to be recognized when the earning process is substantially complete and the amount to be received can unearned revenue be measured reliably, even if the cash has not yet been received. For instance, a software company that has delivered a product and invoiced the client can recognize the revenue even though the payment might be received in the following month. Understanding the difference between revenue recognition and revenue realization is critical for ensuring that revenue is reported accurately. If a company’s revenue reporting is inaccurate, stakeholders may lose confidence in the company’s financial performance and the accuracy of its financial statements. This can lead to a loss of customers, investors, and other stakeholders, which can have a significant impact on the company’s bottom line.